
It's a quantitative test that determines the amount of antigen or antibody in a sample. Where antigen and antibody meet in the right concentration, a precipitate band forms.

Then a parallel trench is made in the gel and filled with a specific antibody solution. Proteins in serum generate separate bands after electrophoresis. Electrophoresis is then used to separate the proteins in the serum. First, a serum containing a protein mixture is deposited in a well on the gel. This method is used to detect and isolate a specific protein in a patient's serum.įor example, to detect a malignant protein combination. In a thin test tube, a transparent sample solution containing antigen is layered slowly, similar to a clear antibody solution.Ī white ring of precipitate occurs at the confluence of two liquids after a specific amount of time. The slide is then turned to thoroughly mix the serum and reagent.Ī positive test is indicated by the formation of precipitate.

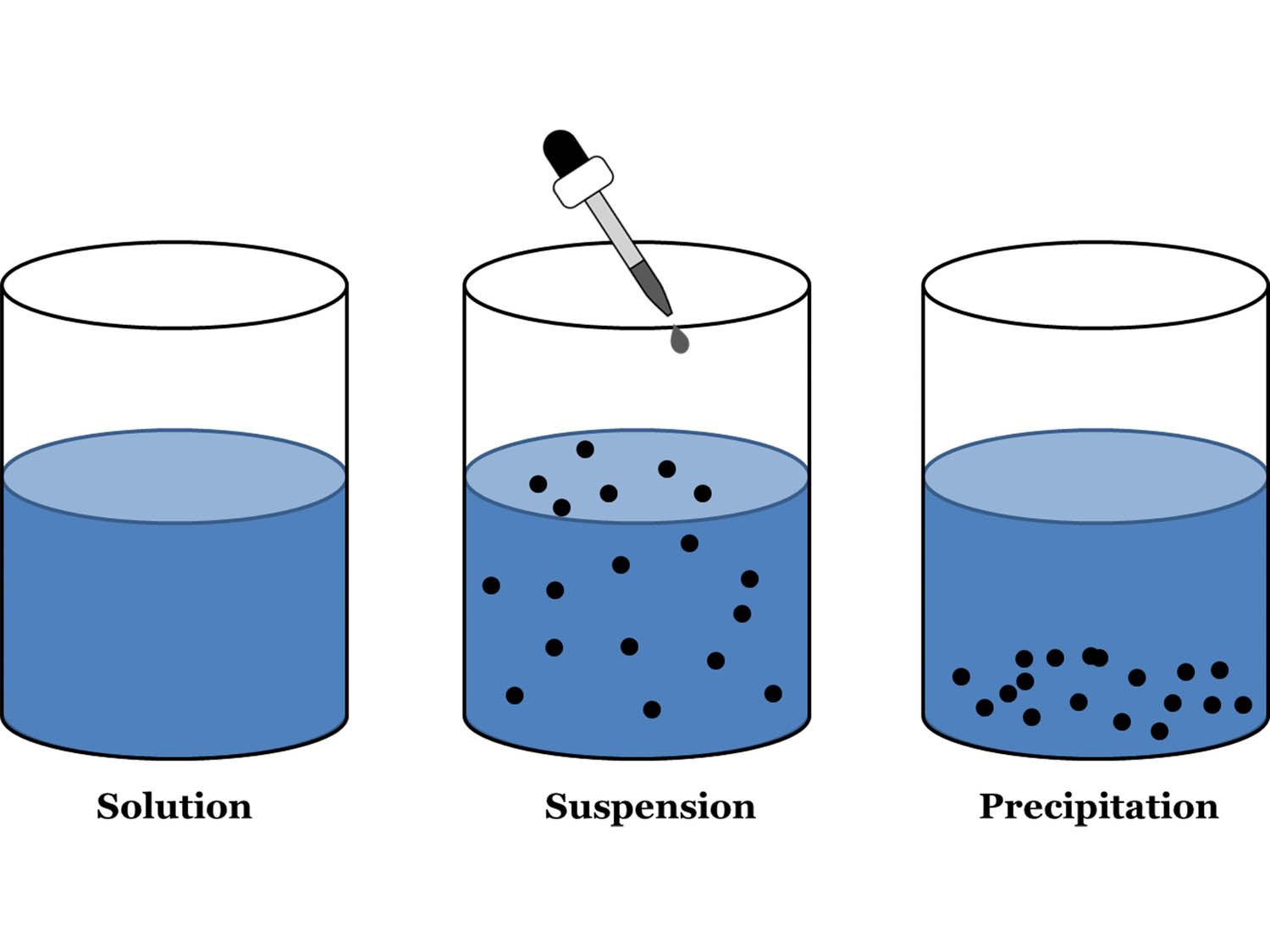
The serum sample is then added one drop at a time. On a slide, one drop of reagent (antigen or antibody) is placed. This experiment is performed on a glass slide. Laws of Chemical Combination for Elements and Compounds.This is the reasons why the precipitate occur only in equivalence zone but not in prozone and post zone. When antigen and antibody are in the proper concentration, maximum cross linking of antigen by antibody occurs, resulting in the formation of a visible precipitate.Įither excess antigen or excess antibody prevents extensive cross linking of antigen by antibody so that visible precipitate is not formed. The lattice hypothesis can be used to explain precipitation formation. Precipitation happens only when antigen and antibody concentrations are in the proper range (4:1)Įquivalence zone is the graph where precipitation happens most frequently. When the antibody concentration is too low and the antigen concentration is too high, however, no apparent precipitate forms.Įxcess antigen inhibits precipitation, which is known as the post-zone effect. Excess antibody inhibits precipitation, which is known as the prozone effect. There is no apparent precipitate when the antibody concentration is too high and the antigen concentration is too low. The flocculation test is performed when precipitate remains suspended rather than sediment.Īg-Ab concentrations must be appropriate for precipitation to occur. When bivalent antibody reacts with multivalent soluble antigen, a visible precipitate forms, which is an antigen-antibody response indicator. A precipitation response occurs in the human body when antigens and antibodies interact. Magnesium is extracted from saltwater using these devices. Precipitation reaction is used to monitor the production of a precipitate in a solution when a chemical is added to it. The precipitation reaction can be used to determine the presence of a certain element in a given solution. As a result, we can add a soluble source of hydroxide (NaOH or Na 2S) to initiate a precipitation reaction. Heavy metals, such as sulphide and hydroxide complexes, are frequently present in wastewater. We can employ this reaction to precipitate out the contaminated ions when a contaminant forms an insoluble solid. In wastewater treatment, the precipitation reaction can be used. Precipitation Reaction Examples in Everyday Life These processes are influenced by temperature, solution concentration, buffer solution, and other factors. Precipitation reactions are referred to as ionic reactions because the ions actively participate in the reaction and generate the product. The precipitates that develop at the end of the precipitation reaction are insoluble in aqueous solutions. The product is formed by a reaction between ions present in aqueous solutions. The precipitation reaction takes place in an ionic state in aqueous solutions or a media.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
